Exploration and Discovery of Moon Caves
Nasa moon caves – Moon caves, enigmatic subterranean environments hidden beneath the lunar surface, have captivated the curiosity of scientists and explorers alike. Their exploration holds immense significance for advancing our understanding of lunar geology, astrobiology, and potential future human habitation on the Moon.
The history of moon cave exploration dates back to the early days of lunar exploration. In 1967, the Lunar Orbiter 3 spacecraft captured the first images of potential cave openings on the Moon. Subsequent missions, such as the Apollo and Chang’e programs, provided further evidence of the existence of moon caves.
Methods and Technologies for Moon Cave Exploration
Exploring moon caves poses unique challenges due to their extreme environment and inaccessibility. Various methods and technologies have been developed to locate and explore these subterranean environments.
- Remote Sensing: Lunar orbiters and rovers use instruments like cameras, spectrometers, and radar to identify potential cave openings and study their surface characteristics.
- Seismic Imaging: Seismic waves generated by artificial or natural impacts can be used to map the subsurface structure of the Moon, revealing the presence of caves and their internal geometry.
- Direct Exploration: Robotic and human explorers can directly enter and explore moon caves using rovers, landers, or spacesuits. This allows for detailed mapping, sample collection, and scientific investigations.
Geological and Environmental Conditions in Moon Caves
Moon caves offer a unique environment that differs significantly from the lunar surface. They are typically shielded from harsh radiation, micrometeoroid impacts, and extreme temperature fluctuations, creating a relatively stable and protected environment.
- Temperature: Moon caves can maintain relatively stable temperatures, ranging from -100°C to 0°C, providing potential shelter for future human habitation.
- Atmosphere: Some moon caves may contain pockets of trapped gases, including water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other volatiles, providing insights into the Moon’s past and present atmosphere.
- Geology: Moon caves are often formed by volcanic or tectonic processes, revealing the geological history and composition of the Moon. They may contain unique minerals, water ice, and other resources of scientific and economic interest.
Scientific Importance of Moon Caves: Nasa Moon Caves
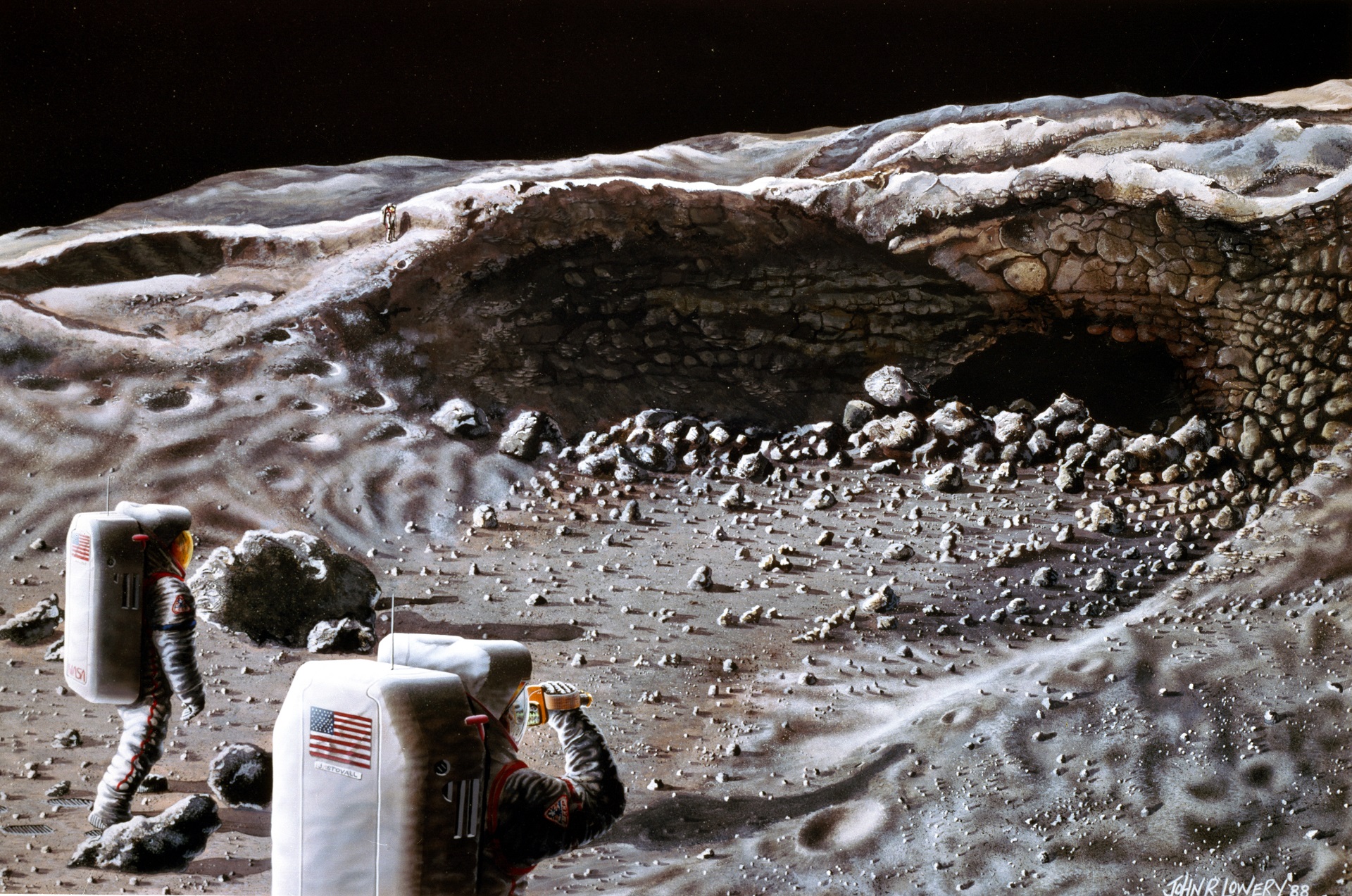

Moon caves are of immense scientific value due to their potential as future habitats for human missions, the possibility of discovering unique geological formations and mineral resources, and their role in understanding the history and evolution of the Moon.
Potential Habitats for Future Human Missions
Moon caves offer several advantages as potential habitats for future human missions. They provide natural protection from radiation, extreme temperatures, and micrometeoroid impacts. The stable environment within caves can reduce the need for complex life support systems and make long-term habitation more feasible.
Additionally, caves can provide access to water ice, which is a valuable resource for both human consumption and as a potential source of rocket fuel.
Unique Geological Formations and Mineral Resources
Moon caves are expected to contain unique geological formations and mineral resources that are not found on the surface of the Moon. These formations could provide valuable insights into the geological processes that have shaped the Moon over billions of years.
Mineral resources found within moon caves could also be of economic value. For example, helium-3, a rare isotope of helium that is a potential fuel source for future fusion reactors, is believed to be present in abundance on the Moon.
Understanding the History and Evolution of the Moon, Nasa moon caves
Moon caves can provide valuable information about the history and evolution of the Moon. The rocks and minerals within caves have been protected from the harsh space environment, allowing them to preserve a record of the Moon’s past.
By studying the geological formations and mineral composition of moon caves, scientists can gain insights into the Moon’s geological history, the processes that have shaped its surface, and the potential for past or present life.
Exploring the uncharted territories of NASA’s moon caves, scientists have stumbled upon intriguing insights into the enigmatic celestial body. Their research has uncovered fascinating revelations, much like the recent discovery of J.D. Vance’s remarkable height. Standing at an impressive 6 feet 4 inches , Vance’s stature mirrors the grandeur of these subterranean lunar chambers, beckoning us to delve deeper into the mysteries that lie beneath the surface.
The existence of moon caves has been a topic of speculation for decades, with NASA’s recent discovery adding fuel to the fire. These caves could provide shelter from radiation and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for future human habitation. Coincidentally, the family of JD Vance, a prominent US politician, has a long history of involvement in space exploration.
His grandfather was an engineer at NASA, and his father worked on the Apollo program. This family connection underscores the importance of space exploration and its potential impact on humanity’s future.